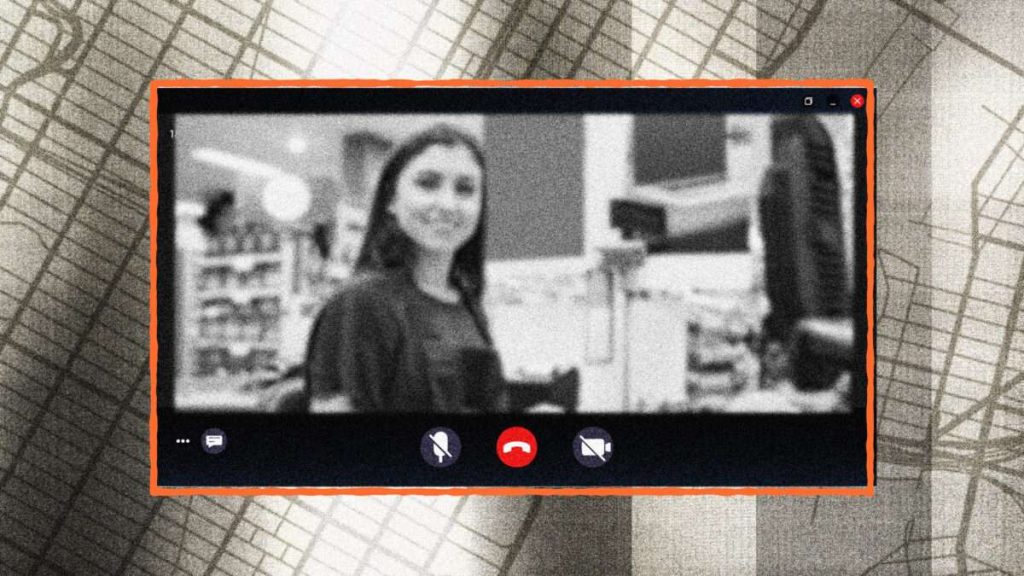
In an innovative move, a chain of New York City restaurants introduced virtual cashiers, who are taking customers’ orders over Zoom from their homes in the Philippines. The approach has sparked heated debates, with some claiming it is a step toward a dystopian, impersonal future. But the technology might not be as bad as critics think.
Customers at Sansan Ramen and Sansan Chicken in the Long Island City neighborhood in Queens are no longer greeted by a cashier face-to-face but instead interact with one displayed on a flat-screen monitor. Although physically half a world away, the virtual cashiers handle menu inquiries and take customers’ orders just like in any other restaurant.
this is insane
cashier is literally zooming into nyc from the philippines pic.twitter.com/opAyS8AYUs
— brett goldstein (@thatguybg) April 6, 2024
The initiative, launched by New York–based Happy Cashier, has been under testing since October. It currently operates in several stores in Queens, Manhattan, and Jersey City, including the dumpling joint Yaso Kitchen.
Yet since the virtual cashiers started trending on social media, the system has faced criticism. A New York Times reporter who visited a Sansan Chicken said the cashier had a spotty connection, making it hard to hear. Another reporter tried to order something off the menu at Yaso Kitchen, but the virtual cashier didn’t seem to know what they were ordering. And a New York Post article seemed to care more about the system’s tipping standards than the benefits of the technology.
Beyond technical glitches, the model has sparked broader economic and social concerns. Critics argue that virtual cashiers are taking away job opportunities from New Yorkers, especially amid the shrinking local fast-food work force. Meanwhile, others have come to the defense of foreign workers who are being “exploited” with a meager salary of $3 an hour—way under New York City’s $16.
Despite these concerns, employing virtual cashiers could have several advantages. For struggling businesses, it offers a way to reduce operational costs and maintain lower consumer prices.
Chi Zhang, the founder of Happy Cashier and a former restaurant owner himself, sees the model as a necessary adaptation. Facing high rents and operational costs, having “a virtual-assistant model, somewhat akin to that employed by overseas call centers, could help maximize small retail spaces and improve store efficiency,” he told The New York Times.
“I simply cannot avoid discussing this topic,” he told Fortune, referring to using outsourced labor to cut down costs. “The cost is admittedly cheaper than the U.S.”
While the operational costs of virtual cashiers are lower for restaurant owners, the wages are also competitive by Philippine standards. According to Zhang, his virtual cashiers are earning over 150 percent more than the average cashier earns back home. It’s a win-win situation.
The concept of virtual cashiers is not entirely new. Back in 2022, the Canadian food chain Freshii hired almost 100 workers from places like Nicaragua to take orders and payments through a video calling device after the company was left grappling with staffing shortages caused by the pandemic.
With the technology still in its pilot stage, improvements are expected. Zhang hopes to quickly scale up the number of virtual assistants by the end of the year, positioning his venture as the leader of a transformative trend in the restaurant industry.
The post Could Virtual Cashiers Be the Future of the Restaurant Industry? appeared first on Reason.com.