Last November, federal prosecutors invited Ilene Wahpeta, an incarcerated woman, to give a victim impact statement at the sentencing of Andrew Jones, a Bureau of Prisons (BOP) employee who was convicted of sexually assaulting three other inmates.
Less than a year later, the U.S. government is fighting a petition Wahpeta filed for early release based on the same allegations that prosecutors previously invited her to speak about, arguing she wasn’t a named victim in the criminal case against Jones and that her claims aren’t credible.
The Justice Department announced in 2022, amid several damning investigations into sexual assault by staff in federal prisons, that it was working to expand a program for early release to include women who’d been abused behind bars, but Wahpeta’s case is one example of what criminal justice advocates say is the Justice Department undercutting that policy. Lawyers representing incarcerated women filing for early release based on their status as sexual assault survivors say federal prosecutors are now routinely fighting to disqualify their clients because of an unreasonably narrow definition.
At the heart of the issue is a new policy passed in April 2023 by the U.S. Sentencing Commission that makes federal inmates who were sexually abused by staff eligible for compassionate release. Compassionate release is a policy that allows federal inmates to petition for early release for “extraordinary and compelling” reasons, such as terminal illness or family emergencies. However, the expansion included a major caveat that was added at the recommendation of the Justice Department. To be eligible, a prisoner’s claim of sexual abuse “must be established by a conviction in a criminal case, a finding or admission of liability in a civil case, or a finding in an administrative proceeding.”
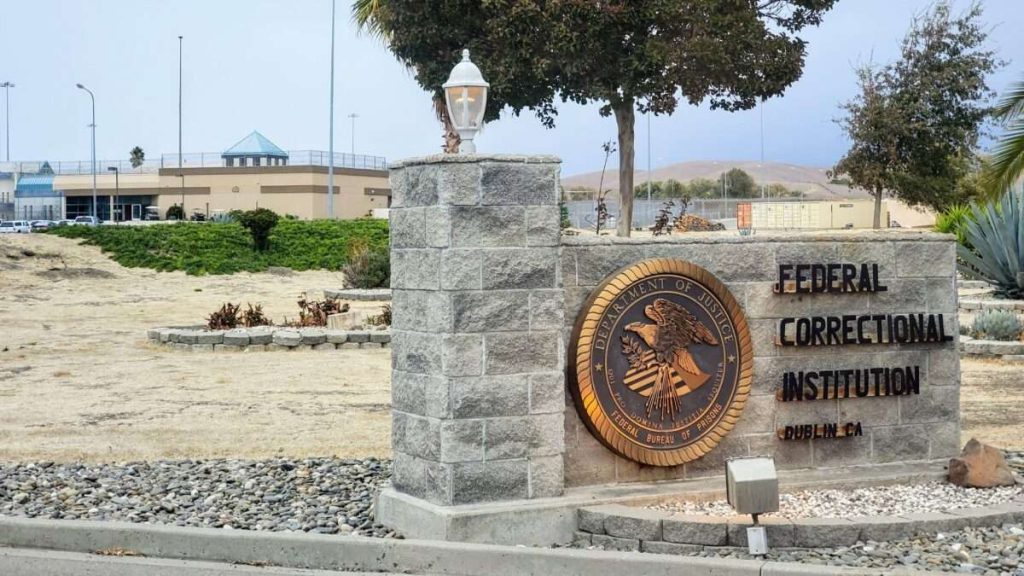
Families Against Mandatory Minimums (FAMM), a criminal justice advocacy group, has been coordinating legal representation for women who were formerly incarcerated at Federal Correctional Institution (FCI) Dublin, a federal women’s prison in California that was infested with so much corruption, sexual abuse, and whistleblower retaliation that the BOP shut it down earlier this year.
Shanna Rifkin, the deputy general counsel at FAMM, says they have secured releases for 17 women out of the 25 cases they’ve taken on. But Rifkin says government opposition has increased significantly since the new policy statement took effect.
“Before November 1, 2023, when this policy statement went into effect, in almost every single case the government was agreeing or not opposing the compassionate release motion,” Rifkin says. “Since then, there has been a lot more resistance to compassionate release motions based on sexual abuse.”
The Justice Department argued that requiring a finding of guilt would set a clear standard for judges. It wrote in a public comment on the Sentencing Commission’s proposed changes that “permitting compassionate release hearings only after the completion of other administrative or legal proceedings will help ensure that allegations are more fairly adjudicated, prevent mini-trials on allegations, and reduce interference with pending investigations and prosecutions.”
However, Rifkin says this undercuts one of the major reforms in the FIRST STEP Act of 2018. That act changed compassionate release to allow inmates to directly petition federal judges, significantly reducing the BOP’s power to stonewall and delay petitions.
“It effectively puts the Department of Justice back in the driver’s seat,” Rifkin says of the new policy statement, “because who drives a criminal case? The Department of Justice. Victims of abuse have no say over when a case against their abuser will be brought, if it will be brought, and who will be charged as the victims in the case.”
And while a finding of guilt may sound like a reasonable standard, it is a surprisingly difficult one to meet in cases of sexual assault perpetrated by government employees.
According to the Bureau of Justice Statistics, from 2016 to 2018, perpetrators of staff sexual misconduct were only convicted, sentenced, fined, or pleaded guilty in 6 percent of substantiated incidents in federal and state prisons.
Reason detailed last year how a cadre of corrupt guards at a federal minimum security camp in Florida was allowed to prey on women for years without oversight. Those guards eventually admitted under oath to internal affairs investigators that they had assaulted incarcerated women, yet most were allowed to retire and none was ever prosecuted.
Over the past year, the Justice Department has ramped up scrutiny of prisons and prosecutions of corrupt BOP employees, but even with more vigilant oversight, criminal cases do not move quickly through the court system, especially if the defendant goes to trial. Rifkin cited one pending case against a former FCI Dublin correctional officer who has been charged with assaulting three women. He was indicted in May 2023, but his trial isn’t scheduled until 2025.
“So women who are survivors of his abuse ostensibly have to wait until the government has concluded their case in order to have a cognizable claim under this policy statement,” Rifkin explains.
As for civil suits against government employees, they routinely take years to resolve, and settlements often stipulate that they do not constitute admissions of guilt by the defendants.
The difference between how petitions have been handled before and after the new standard was enacted is stark. Take the case of Aimee Chavira, a former inmate at FCI Dublin who says she was abused by five correctional officers and continued to suffer retaliation after she was transferred out of the prison.
When Chavira filed her compassionate release petition, only one of those officers had been indicted, and another committed suicide while under investigation. Nevertheless, the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Southern District of California filed a motion of nonopposition in response to her petition. Chavira was released in May of last year.
Contrast that with Wahpeta’s case, where prosecutors have not only tried to apply the adjudication requirement but also attacked her credibility.
In a court filing opposing Wahpeta’s petition, prosecutors note that Wahpeta never gave her victim impact statement because of objections from Jones’ attorney and concerns that her story was insufficiently corroborated. The government also puts significance on the facts that she initially refused to cooperate with FBI investigators and denied being abused; that she didn’t mention being abused in letters to her family she wrote while in solitary confinement; that she contemplated getting a lawyer; and that her descriptions of abuse were remarkably similar to the narratives of the named victims in the criminal case against Jones.
“Even when writing to her parents, her main concern was getting out of confinement early, not reporting what she had seen,” federal prosecutors argue. “Also, defendant never mentions being a victim of abuse, but rather that she witnessed the abuse.”
But this behavior is all too common in cases of sexual abuse in prison. Incarcerated victims of sexual assault often initially refuse to cooperate with investigators out of fear of retaliation from correctional officers, who remain in total control of their lives. Indeed, Wahpeta was put in solitary confinement while Jones was under investigation, and she remained there for more than two months before Jones was removed from the prison. Besides embarrassment or any other number of personal reasons, survivors are also often vague in communications with family because correctional officers can read their letters and emails.
Bay Area news outlet KTVU has interviewed dozens of women over the past two years about sexual abuse and retaliation inside FCI Dublin, and a lawsuit on behalf of multiple incarcerated FCI Dublin women described the repression inside the prison in detail: “Survivors who report sexual abuse are verbally threatened, physically assaulted, sent to solitary confinement, given false disciplinary tickets, have their cells tossed and property destroyed, have their mail (including legal mail) interfered with, strip searched, and transferred to other BOP institutions away from their families—and are even targeted for further sexual abuse.”
In a sentencing memorandum filed in Jones’ case, prosecutors were keenly aware of how retaliation works inside federal prisons. “To enforce the silence that was so critical to the perpetuation of his predation, Jones created an environment of intimidation, fear, and reprisal,” prosecutors wrote. “It wasn’t just words. Jones also enforced silence and obedience through violence and threats of violence.”
Yet, now federal prosecutors take Wahpeta’s silence as a mark against her.
“DOJ has already decided whether Ms. Wahpeta is lying. And it decided she isn’t,” Wahpeta’s attorney wrote in a response. “It decided she isn’t when the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California invited her to read a victim impact statement at Officer Andrew Jones’s sentencing hearing. If the government believed that Ms. Wahpeta was lying, it would have had a duty to tell the Court. It did not do so. In fact, until its response here, at no point during the duration of Ms. Wahpeta’s cooperation with the government has the government questioned what happened to Ms. Wahpeta to either her or her counsel. Nor could it. Because it’s true.”
The Justice Department did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
The post Advocates Say the Justice Department Is Failing To Provide Relief to Women Who Were Abused in Prison appeared first on Reason.com.